What is automatic map alignment?
DroneDeploy's Map Engine employs a computer vision system to align any new map you create with previously processed maps of the same location. This facilitates easy comparison, change detection, use of project overlays, and volumetric measurements.
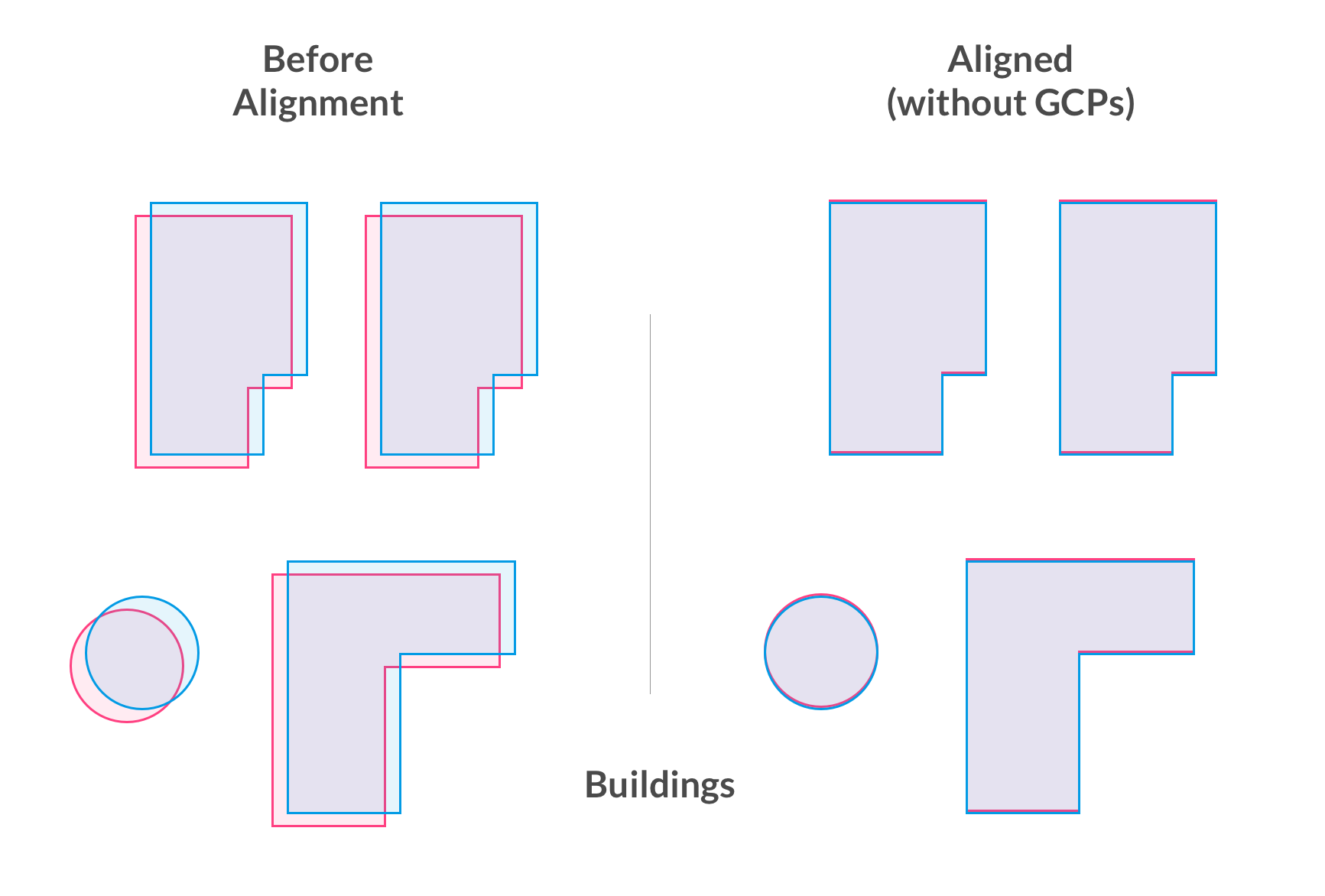
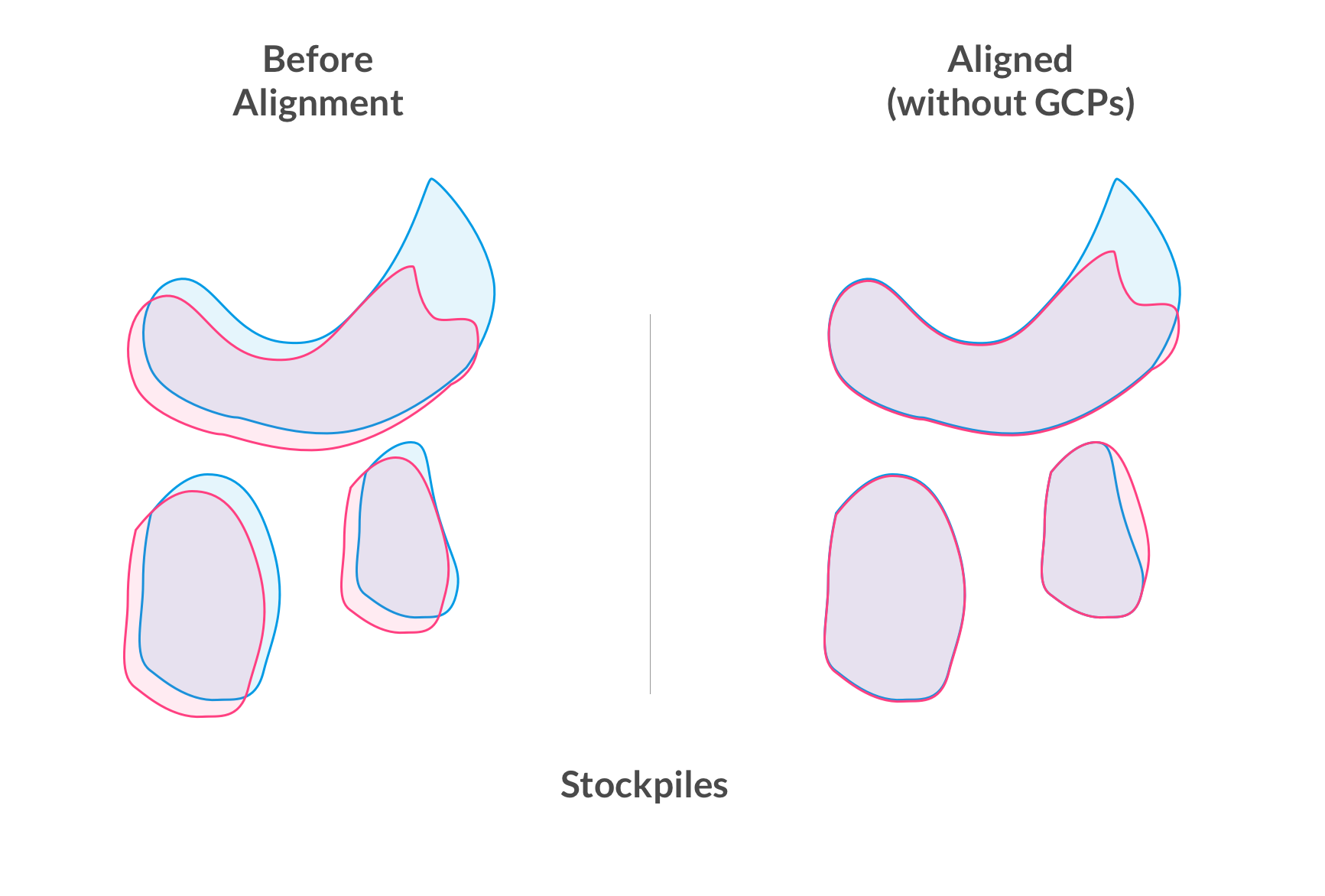
How does it work?
Features of the new map are compared with features from the previous map. If we find the maps similar enough (e.g. most of the scene has not changed), we can usually compute a safe transformation to make the new map align with the previous one.
This means, your maps will align with each other, even without using GCPs.
It also means, if you use Ground Control Points, RTK, or PPK on one map then future maps you create, even without Ground Control, of the same site will gain much of the benefits of Ground Control automatically. This will save you time from laying and picking up Ground Control on every single flight you do.
Best Practices for Automatic Map Alignment
To ensure successful map alignment when repeatedly flying over a single site, it is recommended to use the same flight plan for each mapping session. This includes maintaining consistent overlap, altitude, and waypoints.
Why is map alignment necessary?
In the absence of Ground Control (GCPs, RTK or PPK) photogrammetric data relies on GPS for the scale and alignment of maps with the Earth's surface. However, GPS data may be inaccurate by a few meters. As a result, maps of the same location captured on different days may not perfectly align in 3D space.
Map alignment is crucial for comparing changes over time, reusing blueprint/drawing overlays on multiple maps within the same project, or measuring volumetric changes.
Accuracy considerations
While map alignment offers some advantages of GCPs and RTK, it should not be solely relied upon where high-accuracy measurements are necessary. The only way to confirm the accuracy of your map is by using Checkpoints—either by placing markers at known locations on the map and calculating the error, or by integrating GCPs and Checkpoints.
Application scenarios
General Use:
Map alignment helps keep orthomosaics and elevation models aligned over time. You can reuse project overlays, and compare elevations map-to-map to identify and measure changes without needing GCPs or RTK for each flight.
High Accuracy Mapping:
When significant financial decisions depend on your drone data, use GCPs or RTK alongside Checkpoints. Ensure measurements are conducted accurately—consult your surveyor for guidance. For more details, refer to the American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ASPRS) 2015 standards.
When is map alignment applied?
Map alignment is routinely attempted for each map processed, provided a map of that location has been processed before. The system searches for the most recent map with sufficient overlap, reviewing up to five previous maps. If you would like to see which map your latest map was aligned to, just click the > button next to your map date and read the map date listed beneath "Aligned with map from".
In the example below, the new map on September 2, 2022 was aligned to the previous map from April 2, 2022
When is map alignment not applied?
Map alignment is not applicable to Live Maps, maps with minimal overlap, or when using controlled data such as GCP, PPK, or RTK. It is also not used for thermal maps, and maps flown at significantly different altitudes.
Elevation Alignment
Regular calibration of the drone's IMU/Compass is recommended. When uploading multiple image sets for a single map, ensure they are from the same drone to avoid discrepancies.
Opt-out option
If you prefer not to use our map alignment technology, you can opt-out by contacting our Support Team at support@dronedeploy.com.