What is Cut/Fill Elevation Comparison?
The Cut/Fill comparison toolset allows you to quickly compare the elevation of one map to another map or to a design surface (grading plan).
With heatmap visualization, you can easily identify where soils have been cut or filled from one map to another or how much soil needs to be cut or filled to reach design grade. This allows you to track changes and monitor the progress of earthmoving.
With volume measurement comparison, you can quantify the amount of earth moved (either for an entire site or for individual volume measurements, like a pit or stockpile) so that you can verify subcontractor work, manage stockpile inventory, and better adhere to a project schedule.
Who has access to Cut/Fill Elevation Comparison?
How do I Visualize Cut and Fill?
As long as your project contains more than one map, you will have access to the “Cut/Fill” Map Analysis layer.
When selected, an adjustable color spectrum and elevation bands will appear on top of the map you're viewing. The color spectrum visualizes the elevation difference between your datasets (Map vs. Map or Map vs. Design Surface)
Cut/Fill Map Analysis Layer Overview:
|
|
Cut/Fill Layer First drop-down: map within the project Compare to Second drop-down:
Include trees and other objects (Digital Surface model): toggle ON if you want to include the DSM data Color Spectrum:
Opacity slider: brighten or fade the visualization colors Visualization Range +/-:
Allowed Tolerance +/-:
Data:
Both Cut and Fill will always be shown as positive.
|
Calculations in Detail:
- All volume calculations will be measured as a maximum of an absolute number of CUT or FILL
- Material Volume = absolute |CUT| volume or |FILL| volume.
- If you are measuring a stockpile, your Material Volume = |CUT|.
- If you are measuring a pond or a dip, your Material Volume = |FILL|.
- When comparing datasets, Cut and Fill are expressed in terms of what would need to be cut or filled to match the previous dataset. You can think of this as "proposed cut" and "proposed fill". For example, areas where my map is higher than the design plan would be colored red for "cut", meaning that earth would need to be "cut away" to reach design elevations. The below visual is a good representation of this.
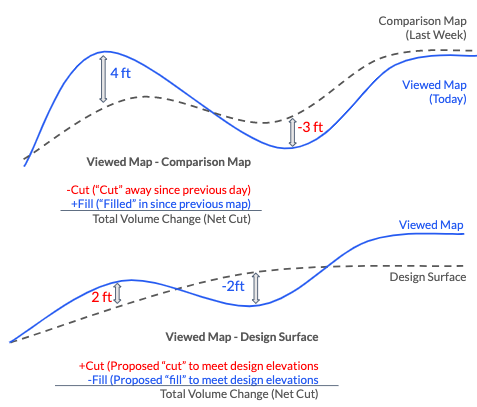
Surface in Detail: Digital Terrain Model or Digital Surface Model
When you view the Cut/Fill layer, you can either compare the Digital Surface Models or the Digital Terrain Models.
- Comparing the Digital Surface Models can be useful to detect differences in structures, equipment, or vegetation from dataset to dataset.
- Comparing the Digital Terrain Models is useful for visualizing changes in terrain due to earthmoving.
Compare to in Detail:
- By default, the color spectrum will show the elevation comparison between the map you are viewing and the previous map within the project, but if you would like to compare to a different map or Design Surface, you can make that selection from the Compare to and Previous Map drop-down lists.
- See: Uploading a Design File for Cut/Fill Analysis & How to Create 2D/3D Visualization DXFs and Design Surfaces in Civil 3D
- The comparison map selected on the Cut/Fill details page will also be reflected in your Cut/Fill Export.
How to Quantify Cut/Fill Using Volume Comparison:
The Cut/Fill details overview shows the total volume difference expressed as Volume to Cut, Volume to Fill, and Total Volume to move, and Net Volume between the two datasets compared (within the area they overlap).
However, the area of overlap may include more than the area of earthmoving that you want to track. Use the Volume Measurement annotation to measure the volume difference between two datasets within a specific area.
Create your Volume annotation and select Previous Map as a base plane.
- Turn on the Cut/Fill layer while making the Volume annotation to help you visualize the elevation difference between the two datasets
Example: excavation area on two different days. When comparing the elevations from each date, you can see that more of the area has been excavated by the second date. We can calculate that over 1,527.95 cubic yards have been excavated in that area between May 4th and August 14th.
Check elevation change at a single point/coordinate using the Location Annotation:
Use the Location annotation to measure the elevation difference between two datasets at a specific geographic point. The Cut/Fill analysis layer, or the Design Surface overlay, must be toggled ON and visible.
Examples of visualizing elevation using the two available layer methods
1. Comparing a single point of elevation between maps
Troubleshooting Tips:
Zoom Level: The zoom level of your Cut/Fill surface is affected by the resolution of your Design Surface. If you notice you cannot zoom past the Cut/Fill layer after a certain point, you will want to upload a higher resolution Design Surface.
GPS & Variations: With default drone map processing, elevations from map to map can vary based on the GPS error of the drone and variations in barometric pressure. This means, the elevation of a point that has not moved may have different elevations on different maps of that point -- and this in turn is a problem for Cut/Fill visualization and volume comparison measurements, which use those elevation values.
- For example, if all of the elevations in your map are a few feet higher than the elevations in your map from Monday, your entire Cut/Fill map would appear red -- not because that much soil has been added but because of the GPS variation from the drone.
Map Processing: DroneDeploy map processing will attempt to correct these issues and align each processed map to previous maps in the same location; however, especially when comparing maps processed before DroneDeploy began automatically aligning maps at the end of 2018, you may still see significant elevation variations between maps.
- Fortunately, there are two ways that you can address these variations. For maps that have already been processed, you can manually correct elevations by using Elevation Calibration to enter the same known elevation at the same point on the different maps that you want to compare. For example, if you know that the corner of the sidewalk is 51.3 ft above sea level, you can enter the elevation at that point on each of the maps you want to compare.
- Another option is to use Ground Control Points and/or RTK/PPK when processing your maps. Especially if you require a high degree of accuracy for your Cut/Fill measurements across a large site. We strongly recommend using Ground Control Points or RTK/PPK to increase the accuracy of your maps and volume comparisons.
Share Your Feedback
Have ideas for Cut/Fill improvements? Please let us know in this brief survey!